Balanced pond fish nutrition concept

Central European standing water bodies, the main part of it consisting of carp ponds, suffer from strong eutrophication (an excess of available nutrients, especially nitrogen and phosphorus). This eutrophication is often associated with the currently conducted feeding (farming) management in these fishponds, which does not consider the balanced nutritional needs of the growing fish. Our present study provides an understanding of how to fish nutrition shapes nutrient excretion and eventually eutrophication. The study concludes that in spring and autumn, the status quo diets lead to inefficient resource use and indirectly to poor ecological conditions. Improved ecosystem resource use efficiency and tackling eutrophication may be achieved by ‘bio-manipulating’ these fishponds towards a more balanced fish nutrition. The study calls for balanced pond feeds that optimize resource utilization efficiency and stimulates fish to exploit better the natural food – in such a way that ecosystem services are maintained.
The authors feel future researchers could carry the baton forward with a novel understanding this article offers. Especially the ecological management of these important pond ecosystems and cleaner aquatic food production from pondscapes of Central Europe.
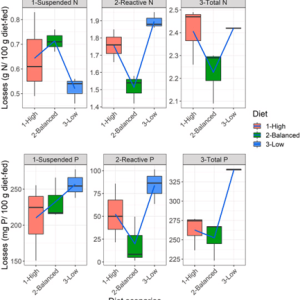
A graphical summary of the presented concept. High= beginning of the vegetative season (lacking carbohydrate energy in ponds). Low= end of the vegetative season (lacking some indispensable amino acids in ponds). Balanced= short transition time (beginning-to-mid summer) when zooplankton-zoobenthos is sufficient and cereals are introduced in a pond. Suspended losses= losses through faeces (undigested nutrients). Reactive losses= losses through gills and urine (discarding of digested nutrients). Nutrient loading from fish stock to a pond ecosystem is minimum when the pond diet is balanced.
Detailed information is available in the original article: Roy, K., Vrba, J., Kajgrova, L., Mraz, J., 2022. The concept of balanced fish nutrition in temperate European fishponds to tackle eutrophication. Journal of Cleaner Production 364, 132584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132584
Written by: Koushik Roy, Ph.D.
Cover photo courtesy: Dipl.-Ing. Tomáš Kolařík